Invokana 100mg canagliflozin ဆီးချိူသွေးချိူ ထိန်းဆေး
Ks118,125.00
Sold out
Selling by
Sold out
Product Details
Brand: Jassen
ဆီးချိူသွေးချိူ ထိန်းဆေး ဖြစ်ပြီး ဆရာဝန် ညွှန်ကြားချက်ဖြင့်သာသောက်ရန်
|
Indications and Dosage
Oral
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Adult: As monotherapy or in combination with other antidiabetic agents: Initially, 100 mg once daily, may be increased to 300 mg once daily if necessary.
|
|
Special Patient Group
Patient taking UGT inducers (e.g. rifampicin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, ritonavir, St. John’s wort): 300 mg once daily, as tolerated.
|
|
Renal Impairment
eGFR 45-<60 mL/min/1.73 m2: Max: 100 mg once daily. eGFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m2, ESRD, patients on haemodialysis: Contraindicated.
|
|
Hepatic Impairment
Severe (Child-Pugh class C): Not recommended.
|
|
Administration
May be taken with or without food. Best taken before the first meal of the day.
|
|
Contraindications
Renal impairment (eGFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m2), ESRD, or patients on haemodialysis. Lactation.
|
|
Special Precautions
Patients with history of hypotension and genital mycotic infection; risk factors for amputation (e.g. prior amputation, peripheral vascular disease, neuropathy, diabetic foot ulcers); CV disease, elevated haematocrit level, risk factors predisposing to ketoacidosis (e.g. pancreatic insulin deficiency, history of pancreatitis or pancreatic surgery; reduction in insulin dose, caloric restriction, severe dehydration, acute medical illness, alcohol abuse, extreme stress event); risk factors for acute renal injury (e.g. hypovolaemia, chronic renal insufficiency, CHF, concomitant use of antihypertensive agents or NSAIDs). Uncircumcised males. Not intended for treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus or diabetic ketoacidosis. Temporarily discontinue therapy at least 3 days prior to surgery. Renal (eGFR 45-<60 mL/min/1.73 m2) and severe hepatic impairment. Elderly. Pregnancy.
|
|
Adverse Reactions
Significant: Bone fracture, hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. angioedema, anaphylaxis), genital mycotic infections (e.g. vulvovaginal candidiasis, balanitis, balanoposthitis), hypotension, hyperkalaemia, UTI (including urosepsis and pyelonephritis), acute renal injury, hypovolaemia, lower limb amputation (mainly of the toe and midfoot).
Gastrointestinal disorders: Constipation, nausea. Investigations: Increased haematocrit, BUN, creatinine, LDL cholesterol. Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Hypoglycaemia (in combination with insulin or sulfonylurea), increased thirst, dyslipidaemia. Renal and urinary disorders: Polyuria or pollakiuria. Reproductive system and breast disorders: Vulvovaginal pruritus. Potentially Fatal: Diabetic ketoacidosis. Rarely, necrotising fasciitis of the perineum (Fournier’s gangrene). |
|
Patient Counseling Information
Adhere to preventive foot care as advised by your physician.
|
|
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor blood glucose and HbA1c (at least twice yearly in patients with stable glycaemic control; quarterly in patients not meeting treatment goals); renal function at baseline and periodically during treatment; serum K periodically (in patients with renal impairment). Assess volume status (e.g. haematocrit, electrolytes, blood pressure) and correct depletion prior to therapy, if necessary. Monitor for new pain, tenderness, sores, ulcers, and infections in the legs and feet; signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis (e.g. nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, shortness of breath, malaise), hypersensitivity reactions, genital mycotic infections, UTI. Confirm diagnosis of ketoacidosis by measuring blood ketones and arterial pH.
|
|
Drug Interactions
May decrease serum concentration with UGT inducers (e.g. rifampicin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, ritonavir). Enhanced hypoglycaemic effects of insulin and insulin secretagogues (e.g. sulfonylureas). May reduce absorption with colestyramine. May enhance hypotensive effects of diuretics. May increase the serum concentration of digoxin.
|
|
Food Interaction
May decrease serum concentration with St. John’s wort.
|
|
Lab Interference
May cause positive result for urine glucose test. May interfere with 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) assay.
|
|
Action
Description: Canagliflozin is a reversible inhibitor of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2), the main site of filtered glucose reabsorption in the renal proximal convoluted tubules. This reduces reabsorption of filtered glucose and lowers renal threshold for glucose, resulting in increased urinary glucose excretion, thus reducing plasma glucose concentrations.
Onset: Within 24 hours (dose-dependent). Duration: Suppression of renal threshold for glucose: 24 hours. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption: Absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability: Approx 65%. Time to peak plasma concentration: 1-2 hours. Distribution: Plasma protein binding: 99%, mainly to albumin. Metabolism: Metabolised via O-glucuronidation by uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)1A9 and UGT2B4 into 2 inactive O-glucuronide metabolites; undergoes minimal oxidative metabolism by CYP3A4 isoenzyme. Excretion: Via faeces (41.5% as unchanged drug, 7% as hydroxylated metabolite, 3.2% as O-glucuronide metabolite); urine (approx 33%; 30.5% as O-glucuronide metabolites, <1% as unchanged drug). Terminal elimination half-life: 10.6 hours (100 mg dose); 13.1 hours (300 mg dose). |
|
Chemical Structure
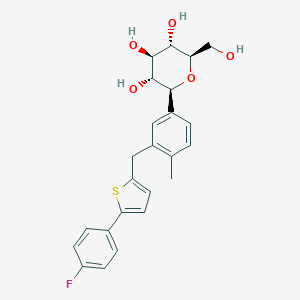
Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Canagliflozin, CID=24812758, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Canaglif... (accessed on Jan. 21, 2020) |
|
Storage
Store between 15-30°C.
|
|
MIMS Class
|
Invokana 100mg canagliflozin ဆီးချိူသွေးချိူ ထိန်းဆေး
Display prices in:MMK